Every month when the BLS releases the employment report, I dig into the data and tweet about it at length using the hashtag #BLSFriday. (Follow me on Twitter to catch this incredibly exciting data dive. The next one is on June 1st.)
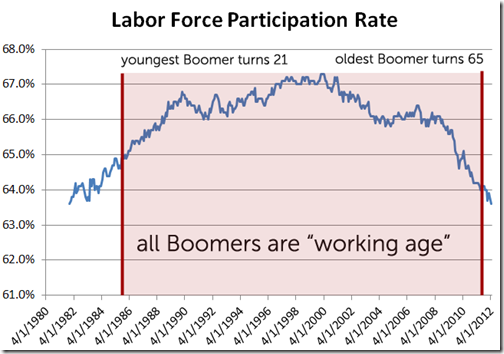
If you’ve been following the job numbers closely, you’ll know that this recession we’ve seen a particularly sharp drop in labor force participation. Labor force participation measures how many people either have a job or are looking for a job as a percentage of the population. As of March 2012 labor force participation has dropped to 63.6%, the lowest point since December 1981.
Because the unemployment rate doesn’t measure people who aren’t in the Labor Force, many (especially conservatives) have noted that the unemployment rate is “artificially” low and that many have left the labor force, basically giving up even looking for a job.
One Twitter friend, @rizzuhjj, pointed out that the Chicago Fed has a paper that claims that half of the post-1999 decline in the labor force is due to long-term demographic trends, specifically, Baby Boomers aging.
Here is a chart of the labor force participation rate since it the last time it was this low. You can see that we’re at the point where Boomers are starting to retire, so surely that would be driving the massive drop in labor force participation and not due to the recession, right?
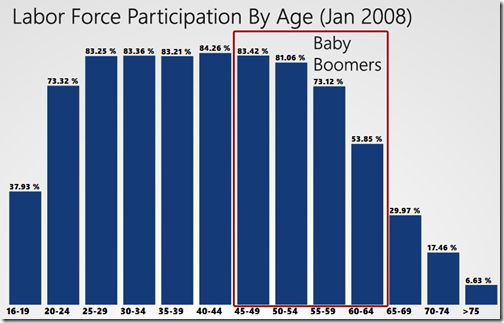
To test this, I decided to sift through the employment data by age, as provided by the BLS. In January 2008, the participation rate by age looked like this (click to enlarge).
(The outline is a rough approximation of where Baby Boomers land in the data. Which is OK because the Baby Boomers are an approximate age group anyway.)
You can see that the boomers are largely entering the age ranges where participation in the labor force drops off significantly. So, on the surface, this explanation makes sense.
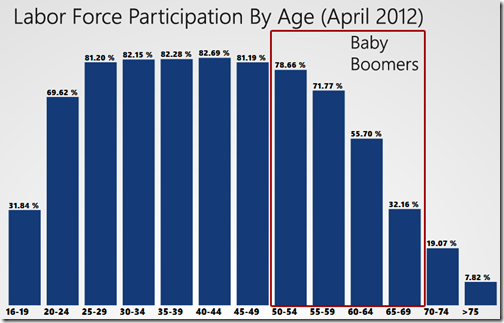
This was my test: Take the participation rates for post-Baby Boomers (16-49 year old) and multiply them for the corresponding populations for those ages. That way we’ve isolated just the post-Baby Boomer labor force and can see if it is smaller now than it was 3 years ago. This is what I found.
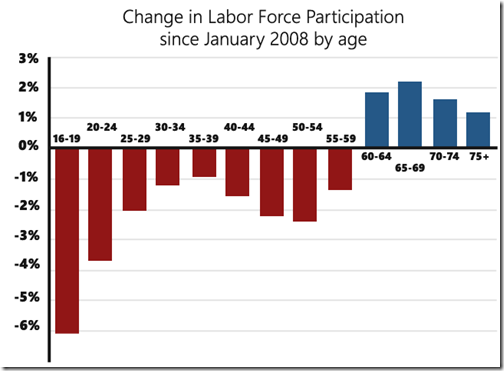
Or, to make it a little clearer, this is the change in labor force participation by age since January 2008.
Apply the January 2008 participation rates to current population and this means we are missing 3.4 million post-Baby Boom workers from the labor force. These post-Boomers account for 68% of the “missing” work force.
If labor force participation was dropping only due to Baby Boomer retirement, the rate should have dropped from 66.2% in January 2008 to 64.8% today. Instead, it is 63.6%. There is certainly a good deal of room for improvement to get younger people back into the labor force. We shouldn’t simply push the problem off to being Boomer retirement or we risk ignoring a whole generation that is unemployed and flying under the radar.